The Mysterious Ocean: Exploring its Depths, Currents, and Ecosystems

The six questions people ask the most about the World's Oceans
What is the depth of the ocean?
The depth of the ocean varies greatly depending on the location. The average depth of the sea is about 3,800 meters (12,467 feet), but it can reach depths of over 10,900 meters (35,760 feet) in specific areas such as the Mariana Trench. The ocean is divided into different zones based on depth, each with unique environmental conditions and ecosystems. The top layer, known as the sunlit zone or the euphotic zone, is the shallowest and is characterized by high light levels and a wide variety of plant and animal life. The deeper layers are increasingly dark and cold, with high pressure and few living organisms.

What causes ocean currents?
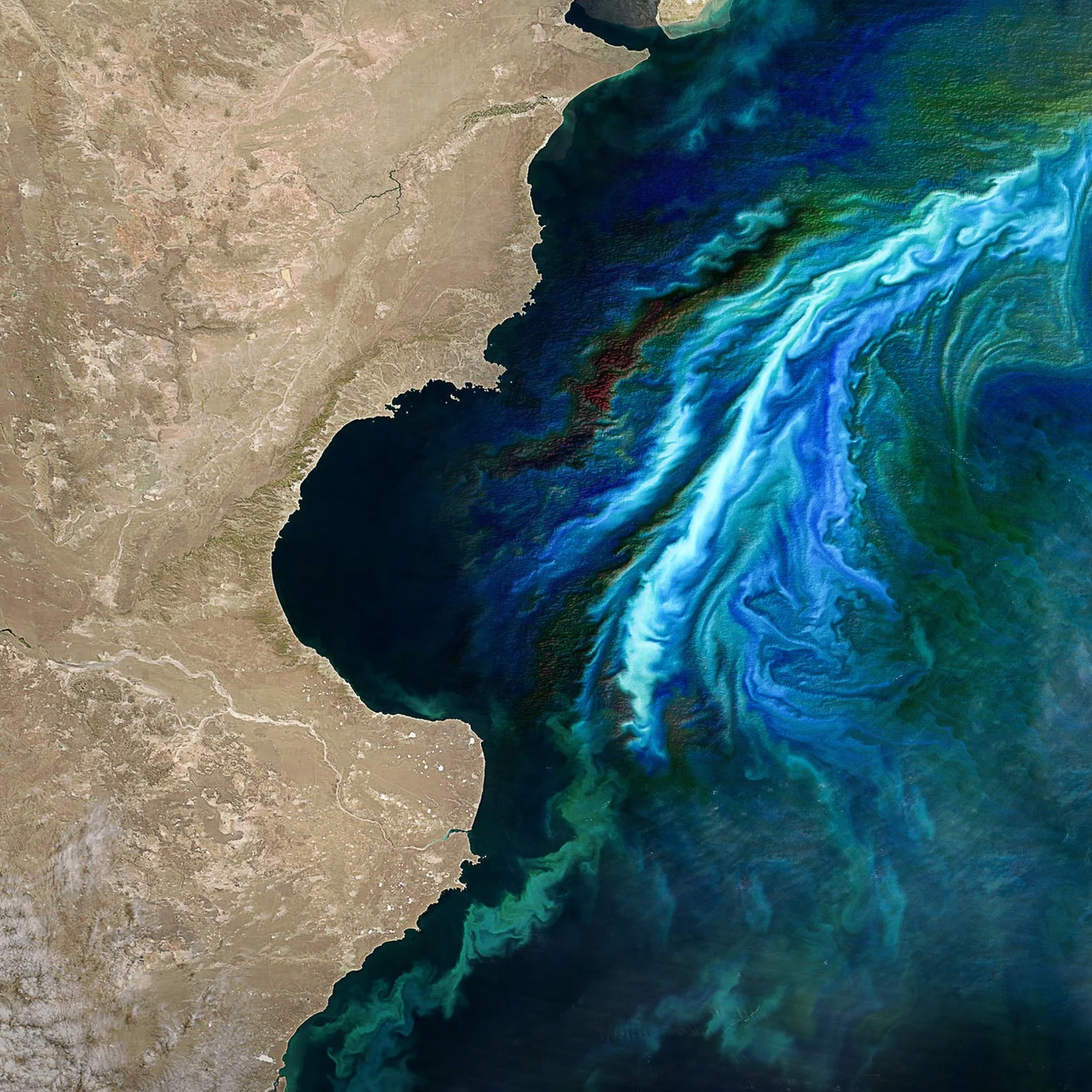
Various factors, including wind, temperature, and differences in water density, drive ocean currents. Surface currents, driven primarily by winds, can move in circular patterns known as gyres. These currents play an essential role in distributing heat around the planet and can significantly impact weather patterns. On the other hand, deep ocean currents are driven by differences in water density caused by differences in temperature and salinity. These currents are much slower than surface currents, but they can move huge volumes of water around the planet and play a crucial role in regulating the Earth's climate.
What is the temperature of the ocean?
The temperature of the ocean varies depending on the location and depth. The ocean's surface is typically warmer than deeper waters, as it is heated by the sun. The average surface temperature of the ocean is around 17°C (63°F), but it can range from below freezing in polar regions to over 30°C (86°F) in the tropics. The temperature of deeper waters is generally colder and more stable, with an average temperature of around 2°C (35°F) at depths below 1,000 meters (3,280 feet).

What is the salt content of the ocean?
The salt content of the ocean, also known as salinity, is about 35 parts per thousand (ppt), which means that for every 1 liter of seawater, there are 35 grams of salt. This level of salinity is maintained by a balance between the input of freshwater from rivers and precipitation and the output of salt through processes such as evaporation and sea spray. Salinity can vary in different parts of the ocean due to factors such as the influx of freshwater from melting glaciers or the mixing of different water masses.

How much of the ocean has been explored?
Despite technological advances, only a small fraction of the ocean has been explored. It is estimated that less than 5% of the world's oceans have been explored in detail, and much of the deep sea remains unexplored. However, scientists are making progress in mapping and studying the ocean through the use of remotely operated vehicles, submersibles, and other technology. These efforts are helping to shed light on the vast and mysterious world beneath the ocean's surface.
How many oceans are there?
There are generally considered to be five oceans on Earth: the Atlantic, Indian, Southern (Antarctic), Arctic, and Pacific. The boundaries between these oceans are somewhat arbitrary and are defined by a combination of geographic, geologic, and hydrologic criteria. The Atlantic Ocean is located between the Americas to the west and Europe and Africa to the east. The Indian Ocean is bounded by Africa to the west, Asia to the north, Australia to the east, and the Southern Ocean to the south. The Southern Ocean encircles Antarctica, while the Arctic Ocean is located around the North Pole. Finally, the Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of the oceans, covering one-third of the Earth's surface.

Places around the world to view bioluminescence in nature: link

Comments